2021 AI Index Report Reveals Light-Speed Innovations
Stanford University's 2021 AI Index Report is now available, and it goes into significant detail regarding Computer Vision, which is integral to the sorts of computing tasks important in check recognition, fraud detection, EOB data conversion, and correspondence letters processing.
Computer Vision is a field of artificial intelligence that trains computers to interpret and understand visuals of various kinds. Using digital images -- still and video -- teamed with deep learning models, machines harness this tech to accurately identify and classify objects, and then react appropriately to what they “see.”

Introduced in the 1960s, the field of computer vision has seen significant progress and in recent years has started to reach human levels of performance on some restricted visual tasks. Common computer vision tasks include object recognition, pose estimation, and semantic segmentation. The maturation of computer vision technology has unlocked a range of applications: self-driving cars, medical image analysis, consumer applications (e.g., Google Photos), security applications (e.g., surveillance, satellite imagery analysis), industrial applications (e.g., detecting defective parts in manufacturing and assembly), and others.
Understanding Image Classification
It is important for readers to understand the concept of "image classification." Analytics India Mag provides a succinct definition:
In simple words, image classification is a technique that is used to classify or predict the class of a specific object in an image. The main goal of this technique is to accurately identify the features in an image.
To put it visually (see image to the right), an image of a cat is classified as a cat.
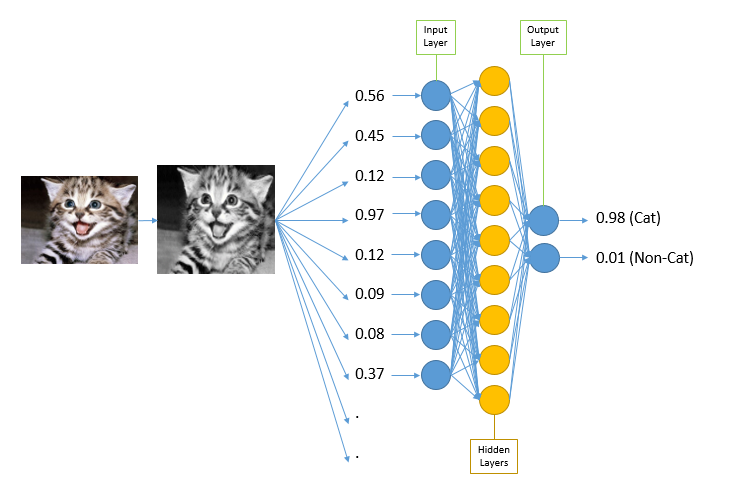
Source: Code Project
Click the image to enlarge.
Check out how google is leveraging image classification for photos:
Image classification is an important component of check recognition, fraud detection, EOB data conversion, and correspondence letter processing. When paper-based images are processed using deep learning models, the fields of the documents need to be properly classified in order to process the data. Furthermore, it directly relates to the identification, recognition, and prediction of the values of the text within the images.
Performance Levels
Later in the chapter, the report notes that image recognition has evolved from being an expensive, domain-specific technology to being one that is "more affordable and applicable to more areas—primarily due to advancements in the underlying technology."
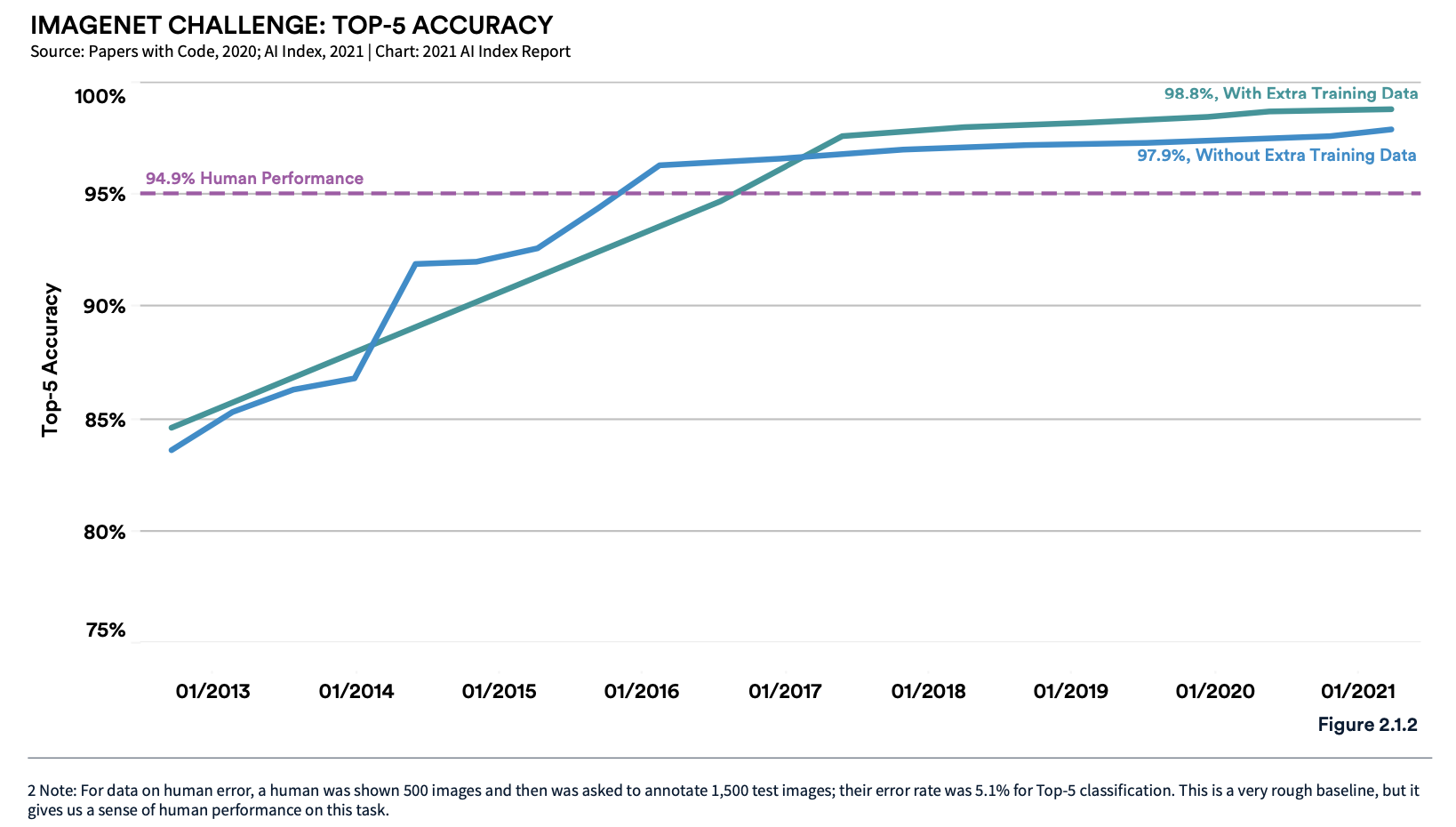
Source: Stanford University
One graph in particular drives home the point. It examines the astounding improvement of ImageNet, a dataset of over 14 million images across 200 classes that expands and improves the data available for researchers to train AI algorithms. In 2013, ImageNet delivered around 85% accuracy -- not bad at all. However, in under 10 years its capabilities have grown to 98.8% when accompanied by extra training data. Impressive as that is, the real milestone can be seen in how quickly it crossed the dotted "Human Performance" line, because that's when real deep-learning advantages are reaped.
As you can see, the advancements indicated in the report are, to say the least, promising -- particularly for the banking and healthcare industries. OrboGraph continues to invest in its OrbNet AI and OrbNet Forensic AI technologies to help the banking industry achieve full automation of check processing, increase detection of fraudulent checks, while also providing the driving technology for automation for revenue cycle.


Check out our OrbNet AI Innovation Lab to see how our technologies can help your organization maximize Computer Vision advances.